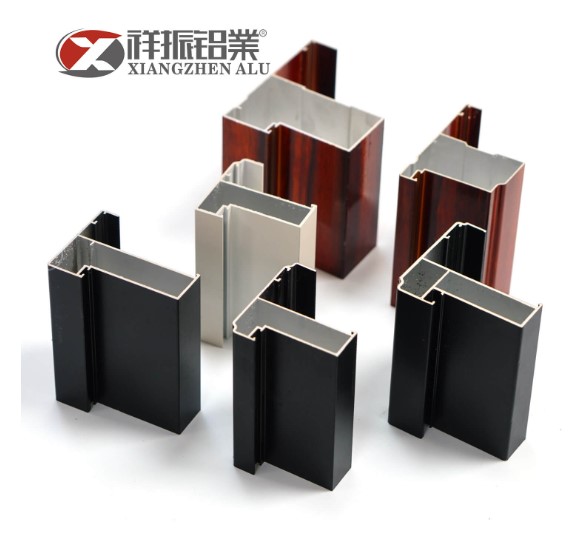

Aluminium profiles are versatile and widely used in various industries, from construction to transportation, due to their lightweight, durable, and corrosion-resistant properties. However, with the numerous varieties, forms, and sizes available on the market, selecting the proper aluminium profile for your unique application might be difficult.
Keep reading this post and get tips about how to choose the proper aluminium profiles.
Generally, aluminium profiles can be categorized into three main groups, based on their manufacturing method: extruded, rolled, and cast profiles.
Extruded profiles are the most common type of aluminum profiles and are produced through the process of extrusion. This method involves heating a billet of aluminum to a specific temperature and forcing it through a shaped opening called a die. The aluminum is pushed through the die, resulting in the desired cross-sectional shape of the profile. Extruded profiles come in a wide range of forms and sizes, offering versatility in design options. They can be simple, such as square or round shapes, or more complex, including T-shapes, U-shapes, and various unique designs.
Additionally, extruded profiles are available in different alloys like 6061, 6063, and 7075, each offering its own set of properties and applications. Extruded profiles are widely used in industries such as construction, automotive, electronics, and furniture due to their flexibility, durability, and ease of customization.
Rolled aluminum profiles are created by passing flat sheets of aluminum through a series of rollers, which gradually shape the material into the desired profile. Compared to extruded profiles, rolled profiles are thinner and more flexible, making them ideal for applications that require bending or curving. The rolling process allows for the production of continuous lengths of profiles with consistent dimensions.
However, rolled profiles generally have a narrower range of cross-sectional shapes and sizes compared to extruded profiles. These profiles find applications in industries such as transportation, packaging, signage, and electrical, where their flexibility and formability are advantageous.
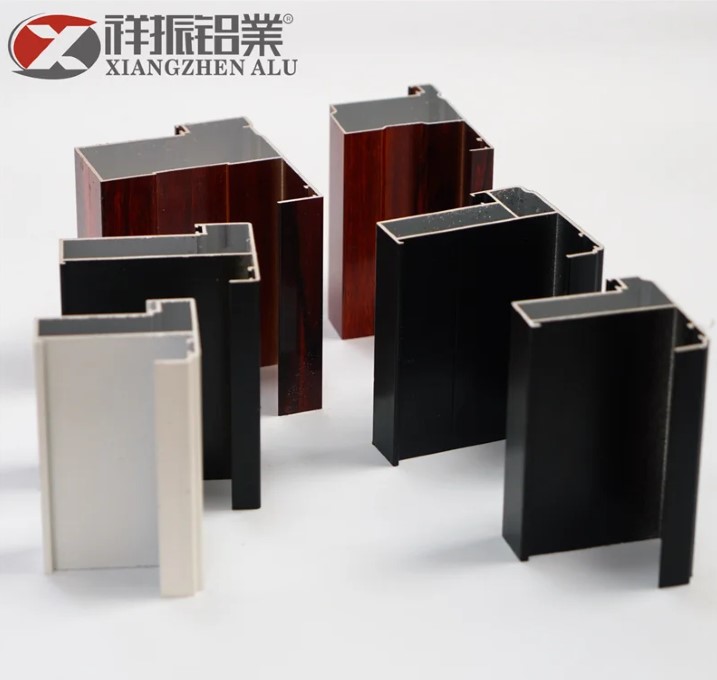
Cast aluminum profiles are manufactured through the casting process, which involves pouring molten aluminum into a mold and allowing it to solidify to the desired shape. Cast profiles tend to be thicker and heavier compared to extruded or rolled profiles. They are particularly valued in applications that demand exceptional strength and durability. Cast profiles are often used in heavy-duty industries such as aerospace, marine, and automotive, where robustness is crucial.
However, cast profiles typically have a more limited range of cross-sectional shapes and sizes compared to extruded or rolled profiles due to the molding process. Despite this limitation, cast profiles excel in applications that require high mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and structural integrity.
When it comes to rolled aluminum profiles, it's essential to dive deeper into their characteristics and applications to make an informed decision. Rolled aluminum profiles are created through a rolling process, where aluminum sheets are passed through a series of rollers to achieve the desired thickness and shape. This technique allows for the production of profiles that are extremely versatile in their use.
The rolling process not only results in profiles that are malleable and adaptable to various applications but also ensures a uniform thickness throughout, which is crucial for applications requiring precision. Rolled profiles are particularly beneficial in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where lightweight yet strong materials are necessary.
In terms of types, rolled aluminum profiles can vary based on the aluminum alloy used, with common types including 1100, 3003, and 5052, each offering different benefits. For instance, 1100 is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and ductility, 3003 offers great formability and is used in complex shapes, while 5052 is favored for its high strength and fatigue resistance.
Moreover, the finishing options for rolled profiles are diverse, providing additional protection against environmental factors and enhancing their appearance. These finishes include anodizing, which increases corrosion resistance, and painting or powder coating, which offers a wide range of color choices.
By understanding the specific attributes and advantages of rolled aluminum profiles, such as their formability, strength, and finishing options, you can better assess their suitability for your project's requirements. Whether you need profiles for structural applications, decorative purposes, or any other specific use, rolled aluminum profiles offer a flexible solution that can be tailored to meet your needs.
Here are some factors to consider when choosing the right aluminium profile:
The choice of material type is a critical factor when selecting an aluminum profile for your application. Aluminum profiles are available in different alloys, each with specific properties that make them suitable for various purposes. Common aluminum alloys used in profile manufacturing include 6061, 6063, and 7075. These alloys offer different combinations of strength, corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and machinability.
Consider the specific requirements of your application, such as load-bearing capacity, environmental conditions, and desired performance characteristics when selecting the appropriate material type.
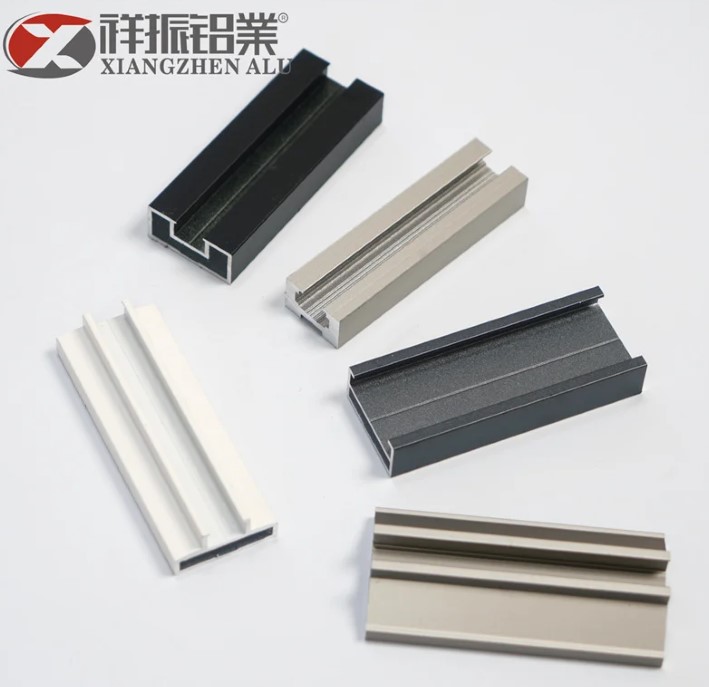
The surface finish of an aluminum profile plays a significant role in its appearance, durability, and resistance to corrosion. Various surface finishes are available for aluminum profiles, including anodized, powder-coated, painted, and polished finishes. Anodizing is a popular surface treatment that enhances corrosion resistance and provides a protective layer on the profile.
Powder coating offers a durable and decorative finish, while painting allows for customization with different colors. Polishing can provide a shiny and reflective surface. When selecting the right surface finish, consider factors such as the intended use of the profile, environmental conditions, aesthetic preferences, and required durability.
The dimensions of an aluminum profile, including its cross-sectional form, size, and wall thickness, can significantly impact its strength, weight, and stiffness. Extruded profiles offer versatility in terms of cross-sectional forms and sizes. Common cross-sectional shapes for aluminum profiles include square, rectangular, T-shape, and U-shape. The selection of the appropriate dimensions depends on the specific requirements of your application.
Consider factors such as the desired strength-to-weight ratio, structural stability, load-bearing capacity, and design constraints when determining the dimensions of the aluminum profile.
When selecting the right aluminium profile, it is also important to choose a reliable and experienced supplier that can provide high-quality products and services. At XIANGZHEN, we offer a wide range of extruded aluminium profiles in different alloys, surface finishes, dimensions, and special features to meet your specific needs. Contact us today to learn more about our products and services.